1. Mitigate Dendrite Growth
Safeguard Battery Stability
The Lithium Dendrite Challenge: From Risk to Control
Lithium dendrites—metallic lithium deposits on the anode—crystallize and grow toward the cathode over time, eventually piercing the separator and causing dangerous short circuits. They’re a critical threat to battery safety and longevity.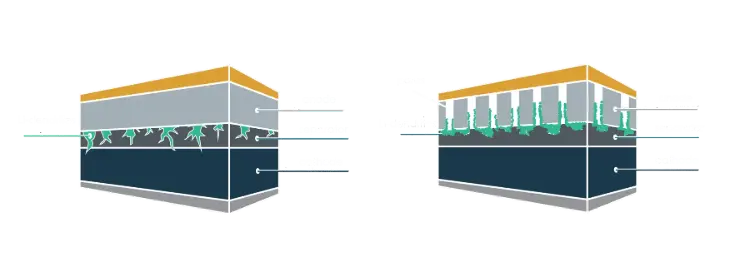
3D PAD’s game-changing technology
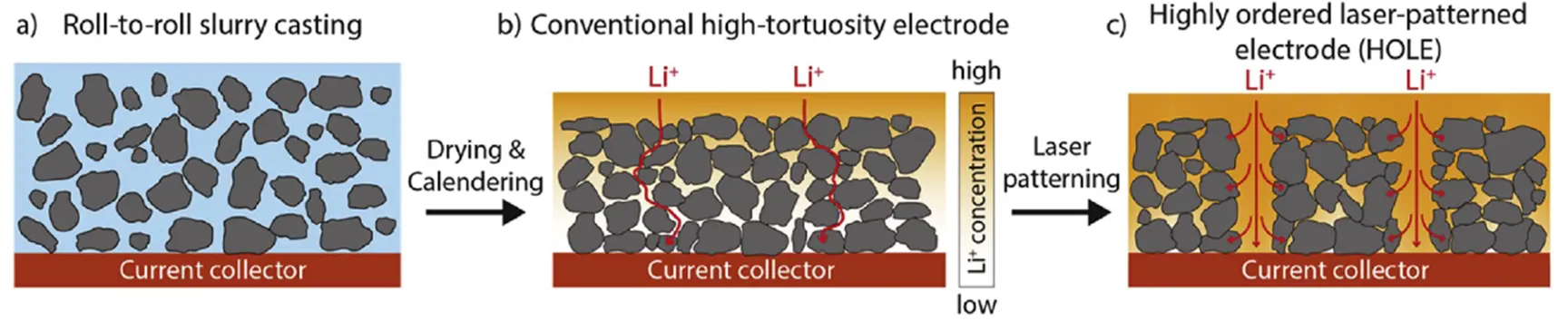
Its engineered channels drastically reduce Li⁺ concentration gradients (see Fig. b), fundamentally curbing dendrite growth. What’s more, expansion is redirected to minimize force on the separator, with extra space allocated for swelling—two mechanisms working in tandem to significantly lower dendrite risks.